As AmeriCorps members are halfway through their service term, tangible evidence of community resilience emerge
CTNC is working alongside our partners to build a network of service throughout North Carolina. The Resilience Service Network brings together the expertise of CTNC, Conserving Carolina, and Conservation Corps NC to leverage the investments of AmeriCorps to build capacity of nonprofits, local governments, and agency partners to achieve resilience.
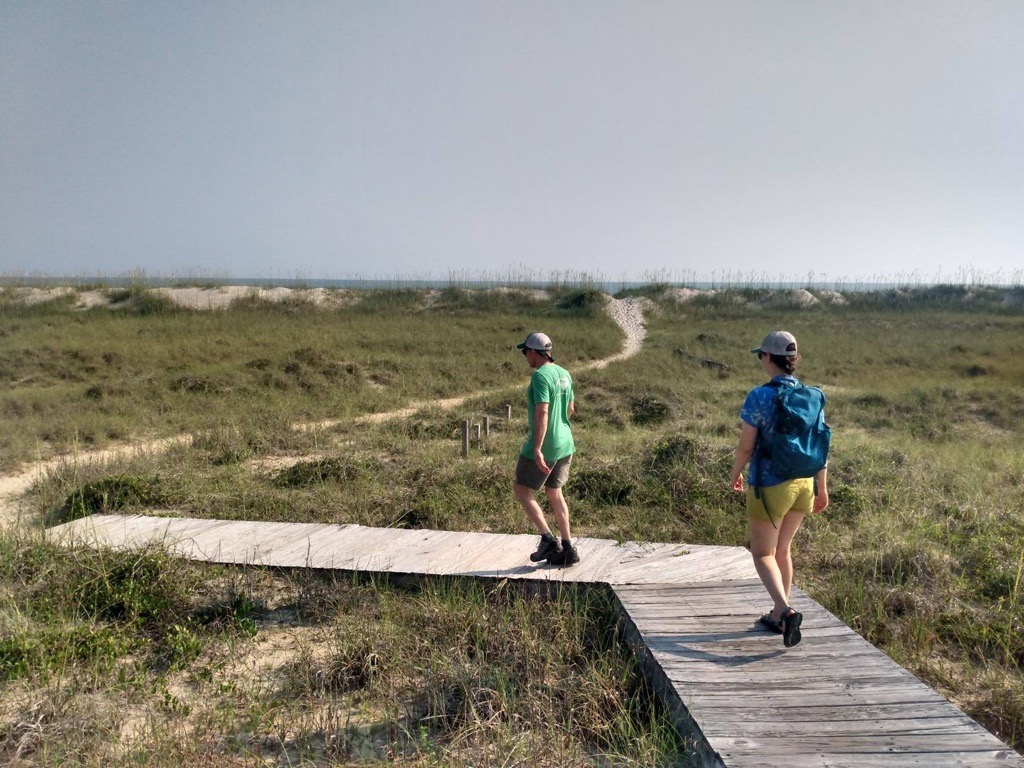
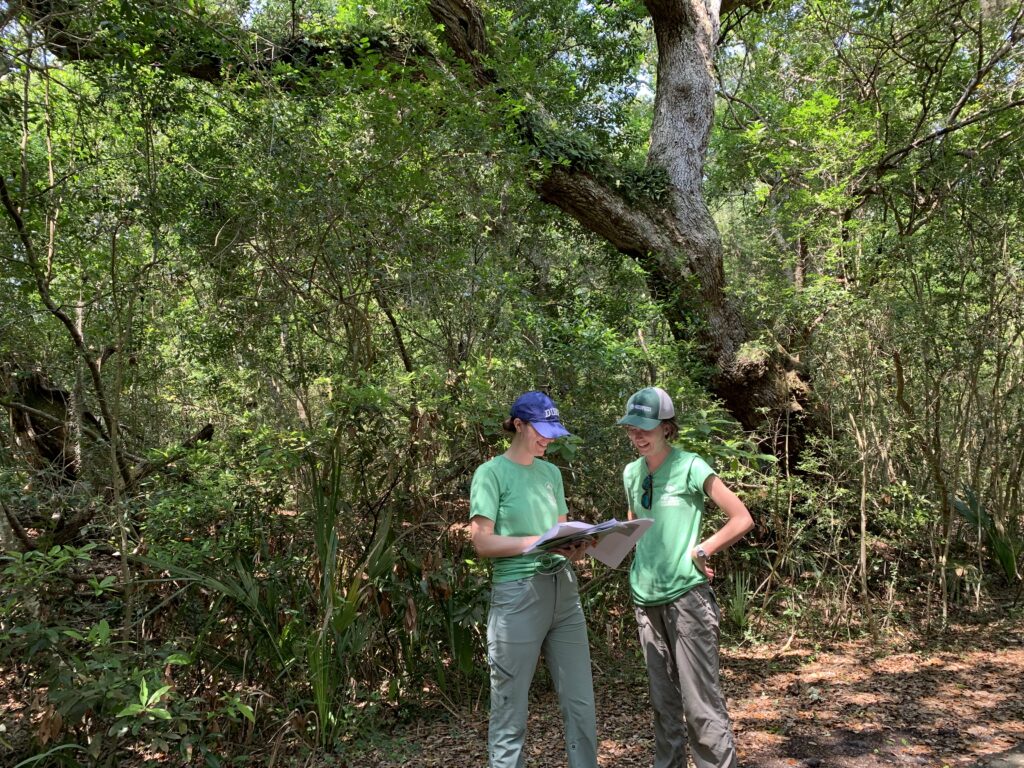
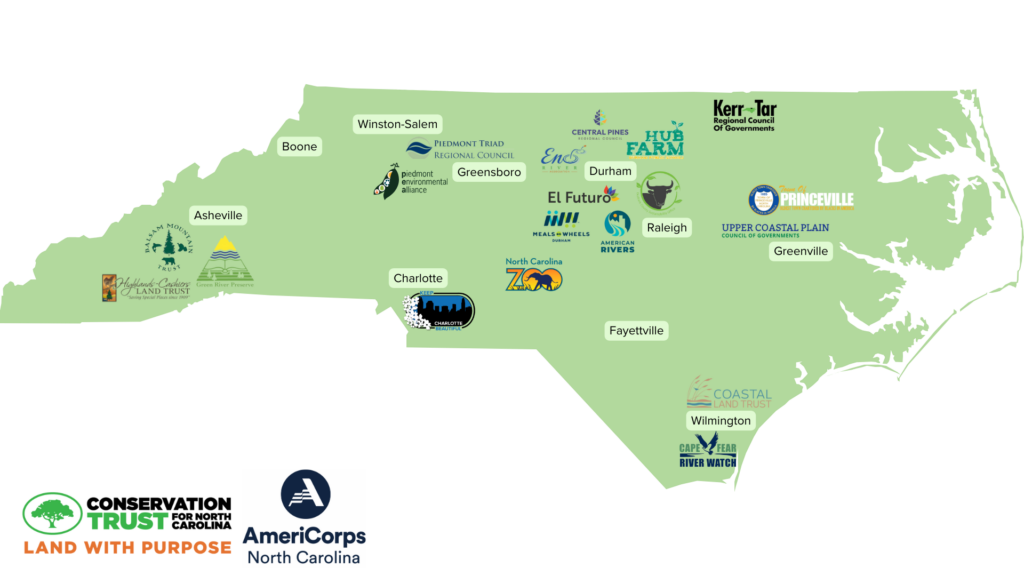
CTNC’s AmeriCorps program, Resilience Corps NC, has partnered with 20 host site partners to deploy 23 members in service to communities with climate risk and capacity needs. These members are now halfway through their service term, which began in September of last year. With members serving in over forty communities across the state, tangible evidence of community resilience is present.

How do we select these community partners? CTNC seeks to prioritize community partnerships where a high climate-risk to flood, fire, food insecurity, or urban heat effects is affecting socially vulnerable communities and people throughout North Carolina. Using data assessments found in our Community Resilience Model, a GIS map that pinpoints the communities of NC that could benefit the most from climate change resilience work, we can ensure our AmeriCorps partnerships are delivering on CTNC’s goals to build resilience throughout the state.
See where our partnerships are growing resilience:
| Anna Behnke Conservation Trust for North Carolina Communications & Outreach Associate | Austin Duncan Central Pines Regional Council Stormwater Education Coordinator | Charlie Robinette Kerr-Tar Council of Governments Resilience Project Coordinator | Christopher Perdomo Piedmont Environmental Alliance Environmental Educator |
| Cindy Rassi El Futuro Community Engagement & Therapeutic Green Space Coordinator | Crystal Nowell Durham County Sustainability Office Community Stewardship Coordinator | Eli Haines-Eitzen Eno River Association Education Program Coordinator | Ellen Davis Central Pines Regional Council Community Development |
| Gina Patton Balsam Mountain Trust Education Outreach | Grace Sigmon North Carolina Zoo Natural Areas Conservation Educator | Haley Bock Piedmont Triad Regional Council Environmental Programs | Hannah Nystrom Cape Fear River Watch Resilience Project Coordinator |
| Hannah Rhodes American Rivers Resilience Project Coordinator | Jessica Blackburn Highland-Cashier Land Trust Environmental Education | John Sugg Upper Coastal Plain Council of Governments Resilience Project Coordinator | Jordan Pilcher North Carolina Coastal Land Trust Education & Volunteer Coordinator |
| Lauren Howard Green River Preserve Education Member | Lauren Waibel North Carolina Coastal Land Trust Stewardship & Community Conservation Coordinator | Lula Zeray Meals on Wheels Durham Volunteer Services Associate | Rae Cohn The Hub Farm Educator & Farm Member |
| Sabrinah Hartsell North Carolina Zoo Nature Rock’s & Virtual Programming Assistant | Tanya Balaji Keep Charlotte Beautiful Engagement & Education Specialist | Tykia Lewis Town of Princeville Outreach Coordinator |
The Resilience Service Network Case for Support demonstrates the need for additional capacity in vulnerable communities across the state. By building capacity in partnership with local leaders, the work being accomplished by these members will successfully increase the capacity of what each organization can accomplish.
Resilience Corps NC members have built capacity at each of their host sites, whether it be tree planting, organizing volunteer events, community outreach and engagement, land monitoring, environmental education, climate change education, and many other projects designed to seed future resilience.
CTNC is proud to champion the movements completed by the Resilience Service Network. Advancing community resilience through building relationships and partnerships is a critical component of all conservation efforts. Having members placed in all regions of the state, Western, Piedmont, Central, Eastern and the Coast, ensures that vulnerable communities are both represented and included in statewide conservation initiatives.