A floodplain reimagined into a community garden takes root
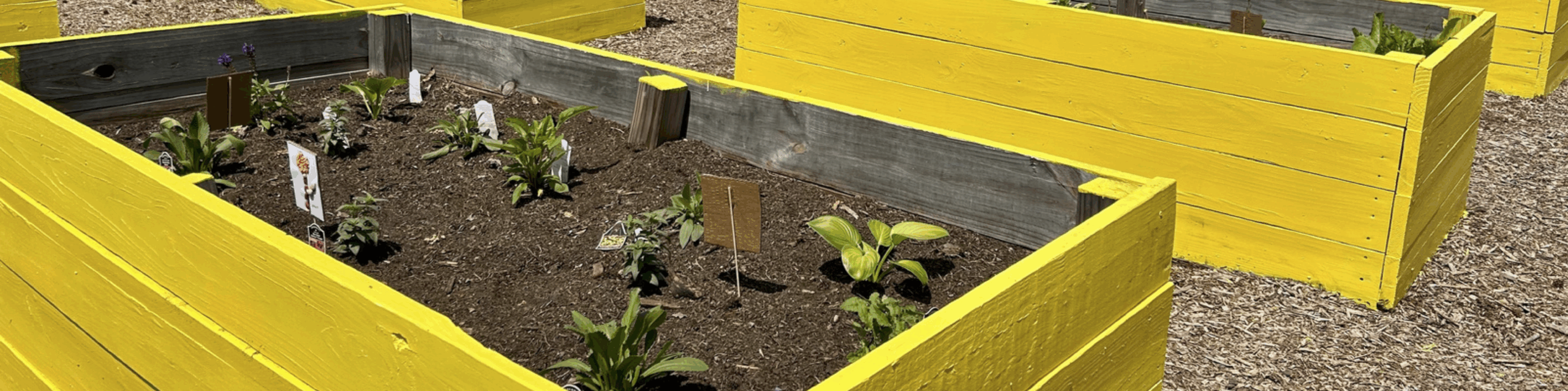
On April 19, Princeville, NC celebrated an exciting milestone with the opening of the Princeville Community Garden. With nearly 70 community members coming and going throughout the day, the event was a joyful celebration of collaboration, connection, and growth.
The opening event featured grilled food, garden-themed kids’ activities, a seed giveaway, and an art display featuring the creative talents of Princeville Elementary students. The exciting and collaborative day couldn’t have been made possible without the support of the Town of Princeville, Resilience Corps NC, Freedom Org, MOSS Kids, Princeville Elementary. Catering was provided by Big Bones Meat Market, My Jnlle’Z, and SuSu & Kizzie’s Sweet Treats.
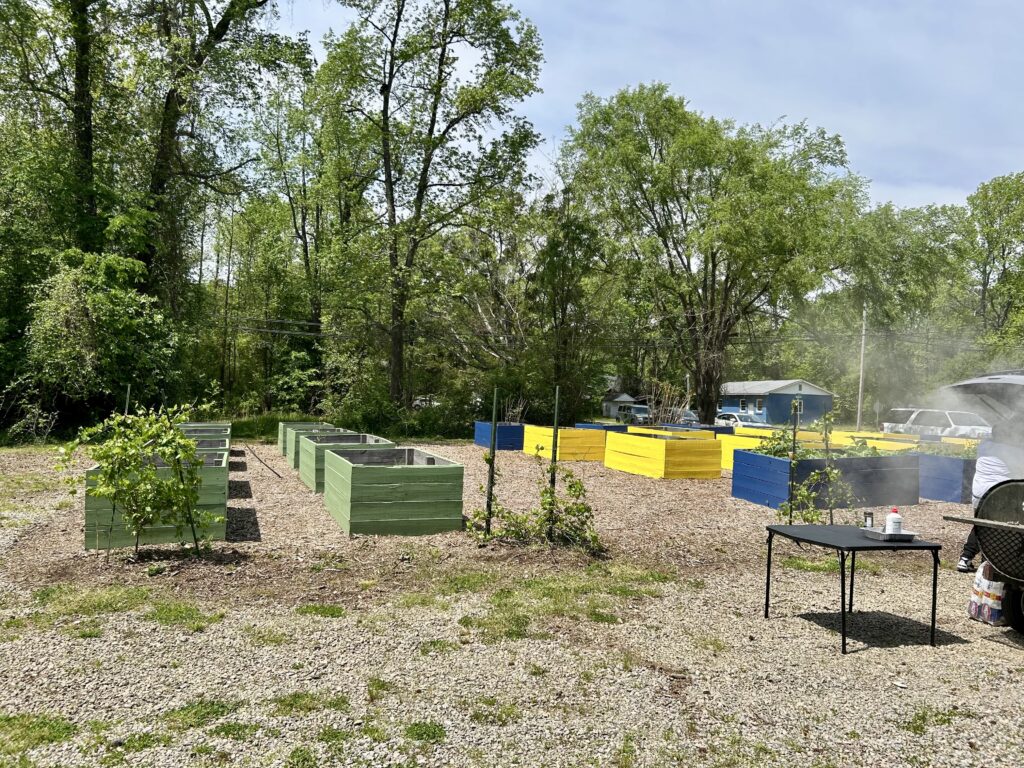
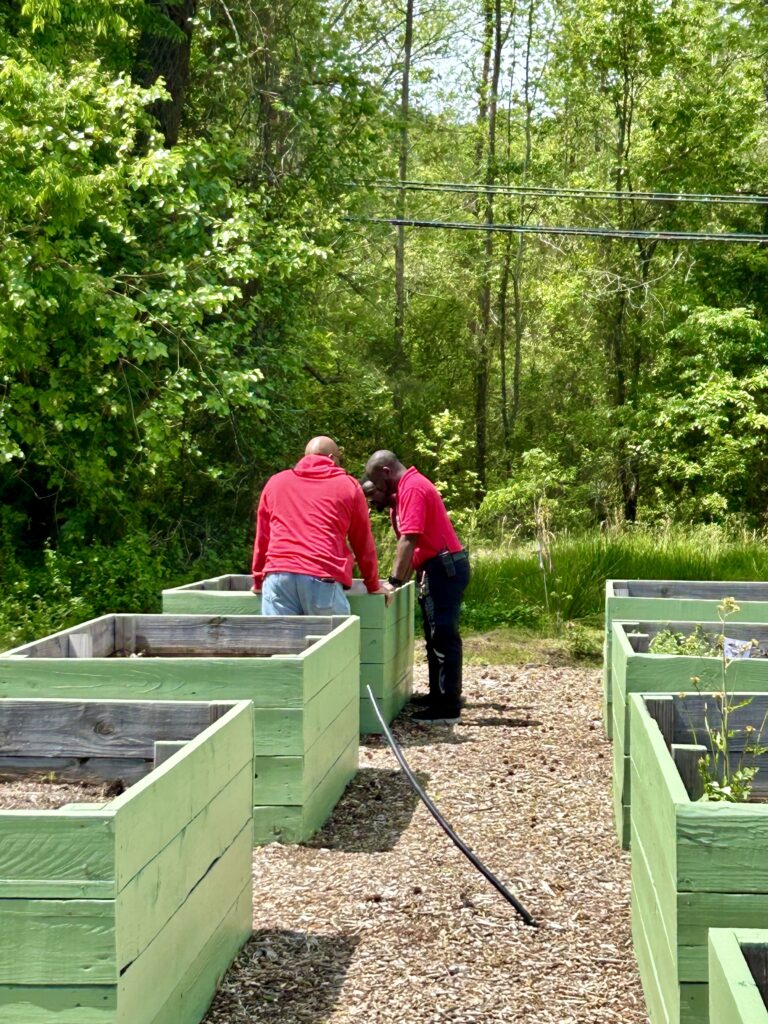
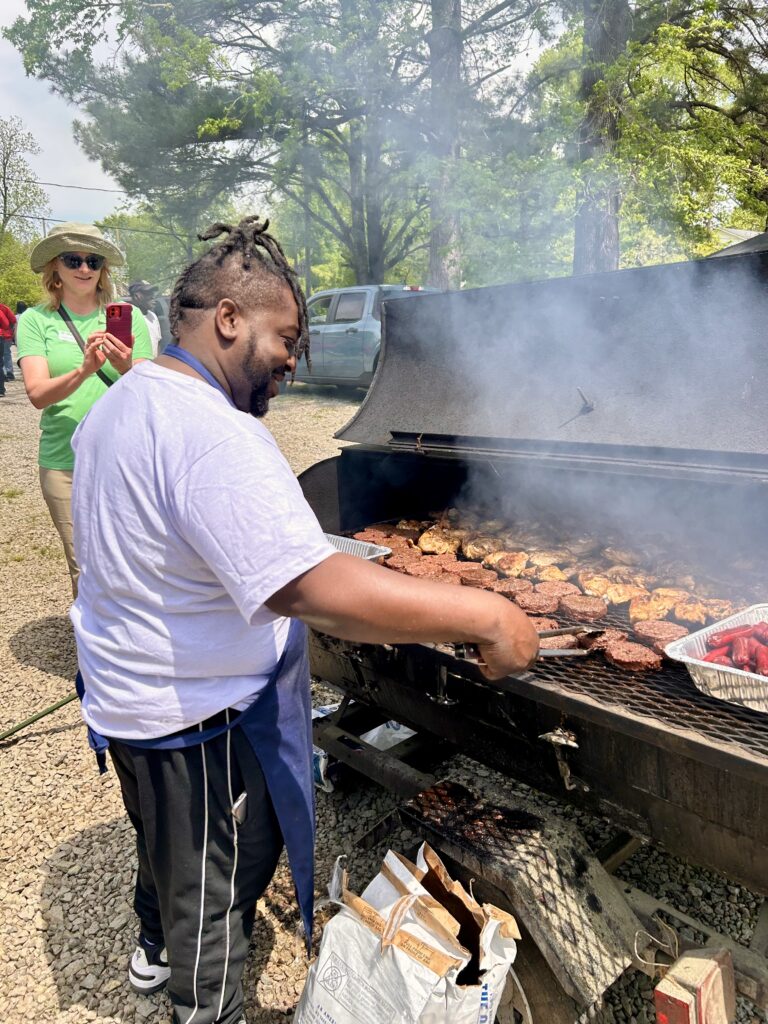



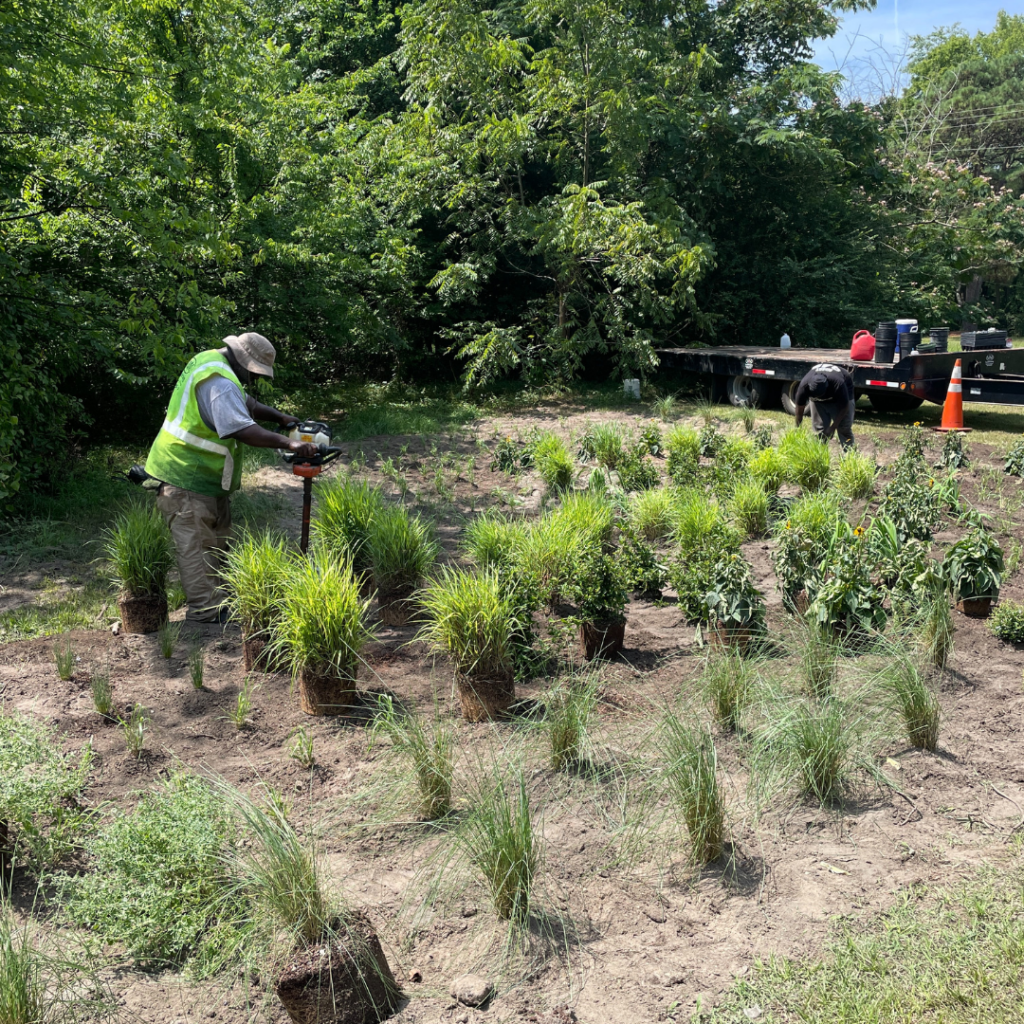
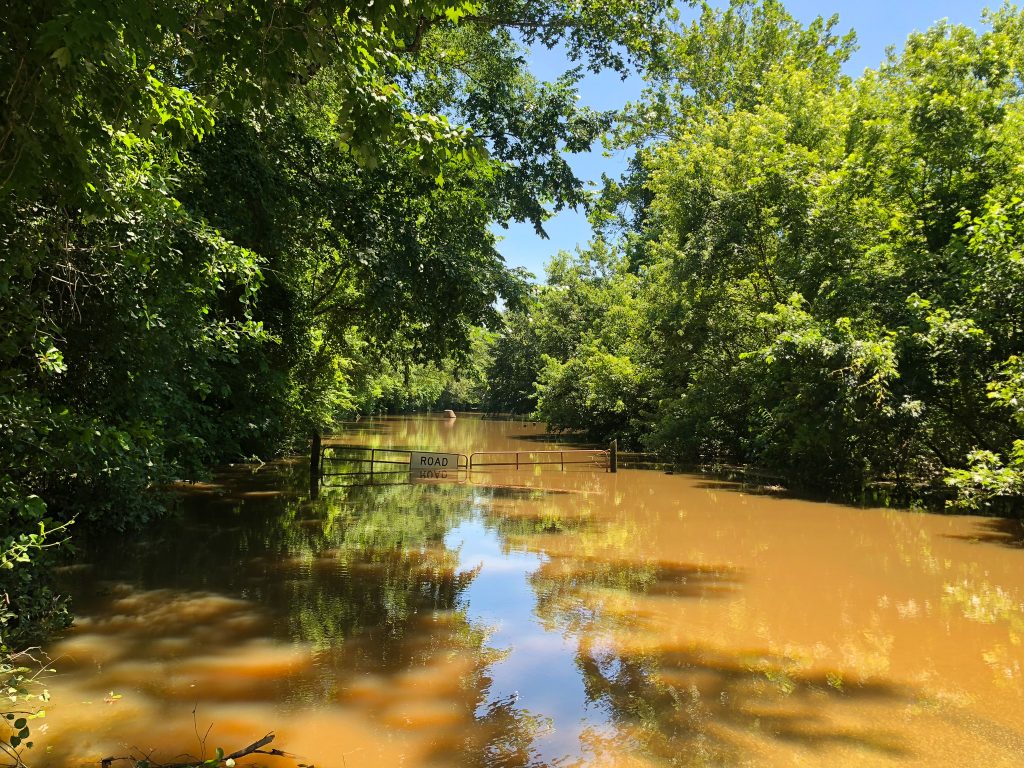
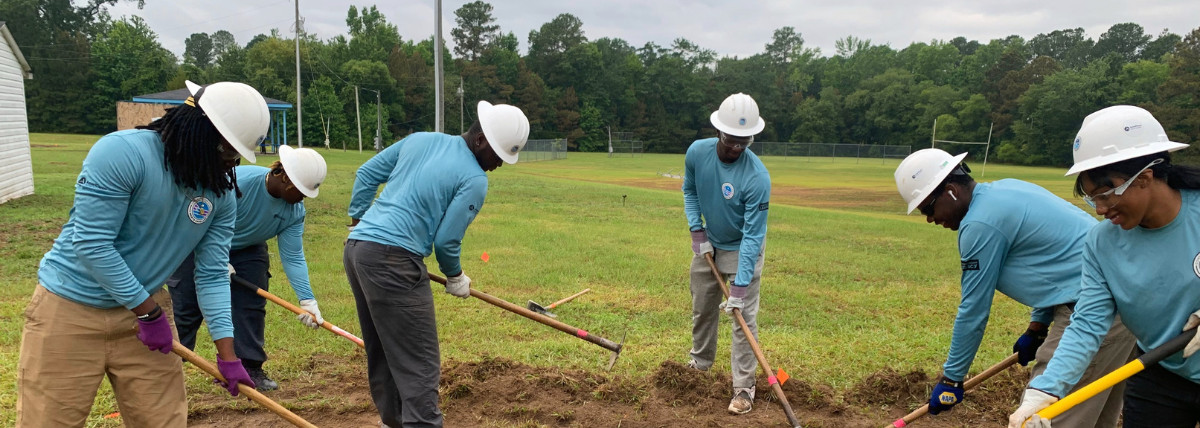
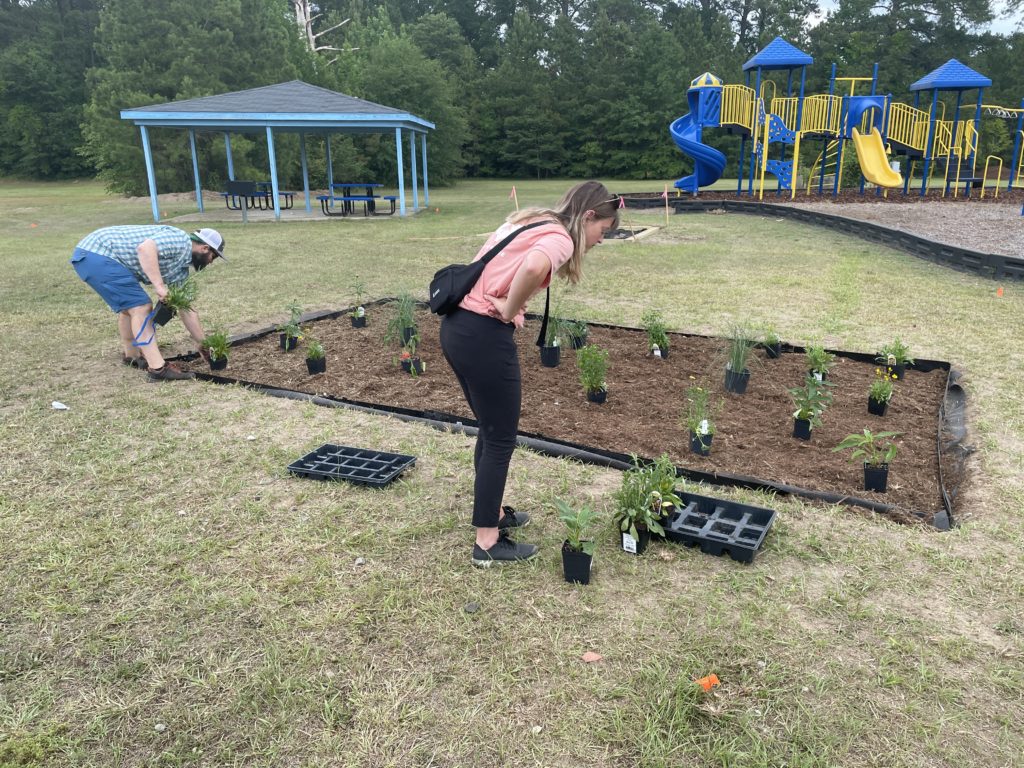
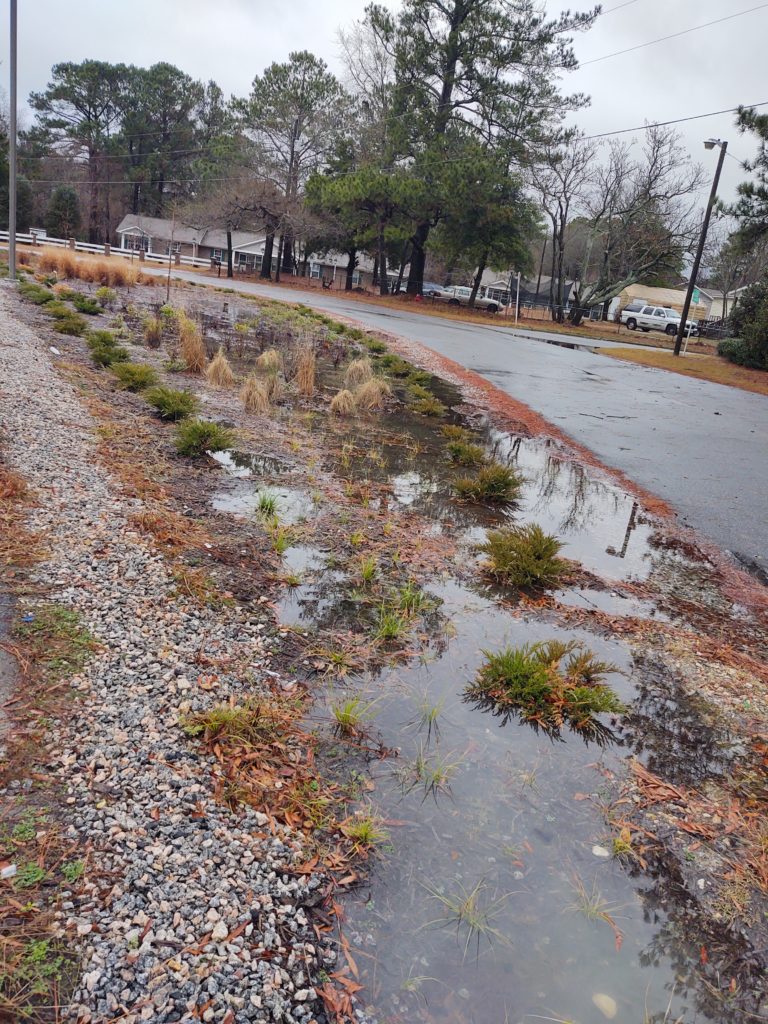
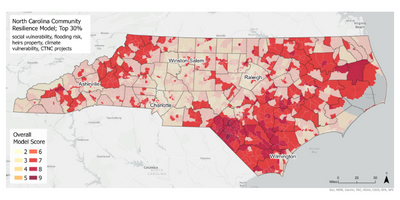
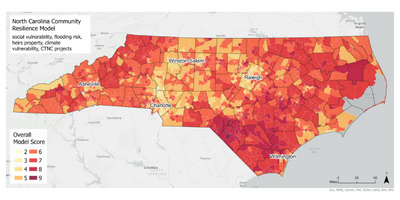
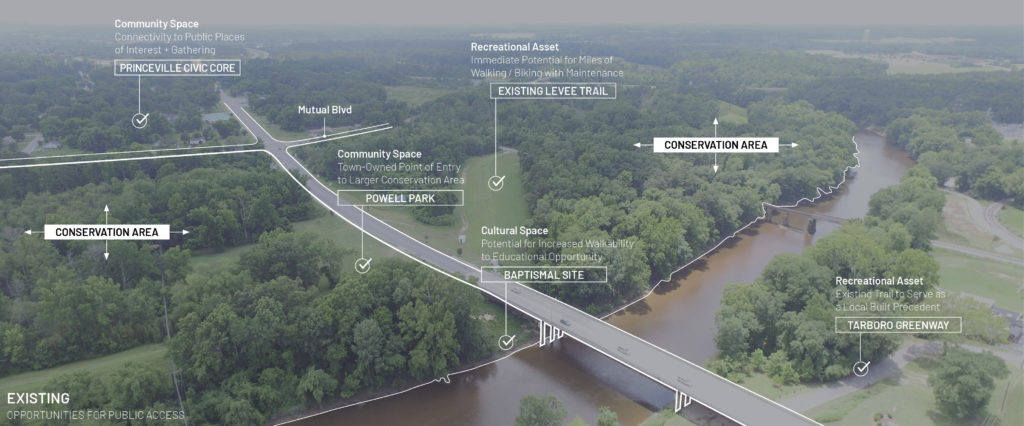
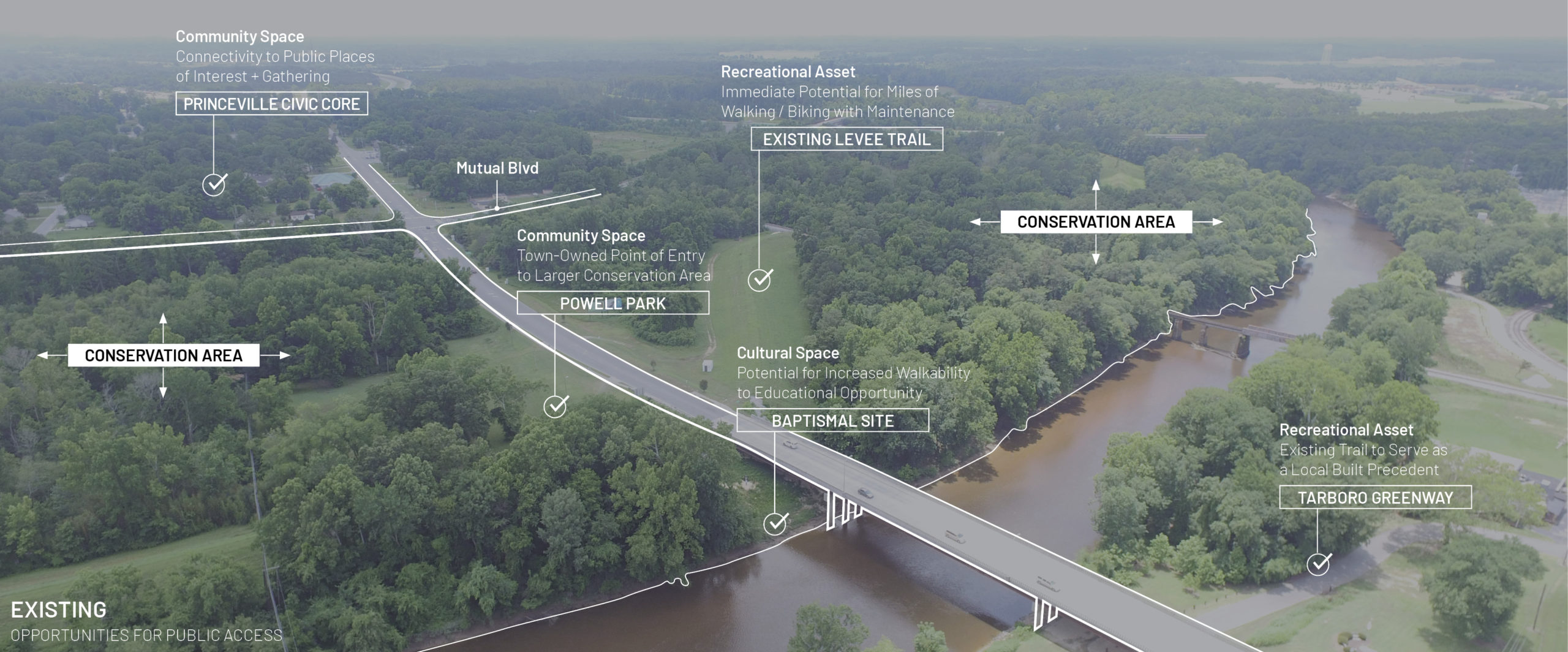
The garden itself represents more than a place to grow food. It’s the result of years of thoughtful planning and collaboration. The garden is a key outcome of the land use plan developed in partnership with the NC State Coastal Design Lab and Town leaders. Located on land purchased through FEMA’s buyout program, this area could no longer be developed for commercial or residential use, but thanks to the vision of leaders and residents in Princeville, it’s now a vibrant community space.
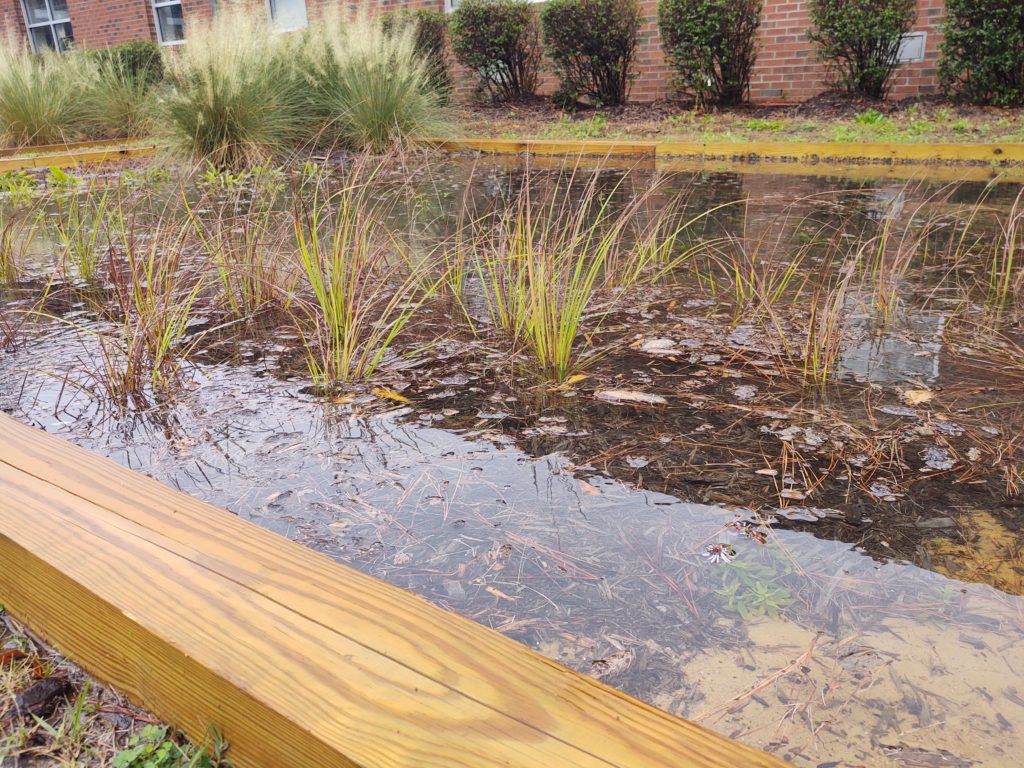
The garden also stands as a reimagined nature-based solution to mitigate flood damage and restore the land to a meaningful and productive use. To support stormwater management, the garden space will act as a rain garden as well. This is especially impactful as Princeville is located in a vulnerable region along the Tar River with devastating flooding events in the past. With this parcel of land reconstructed into a community garden, the benefits exceed just harvesting fresh fruits and vegetables.
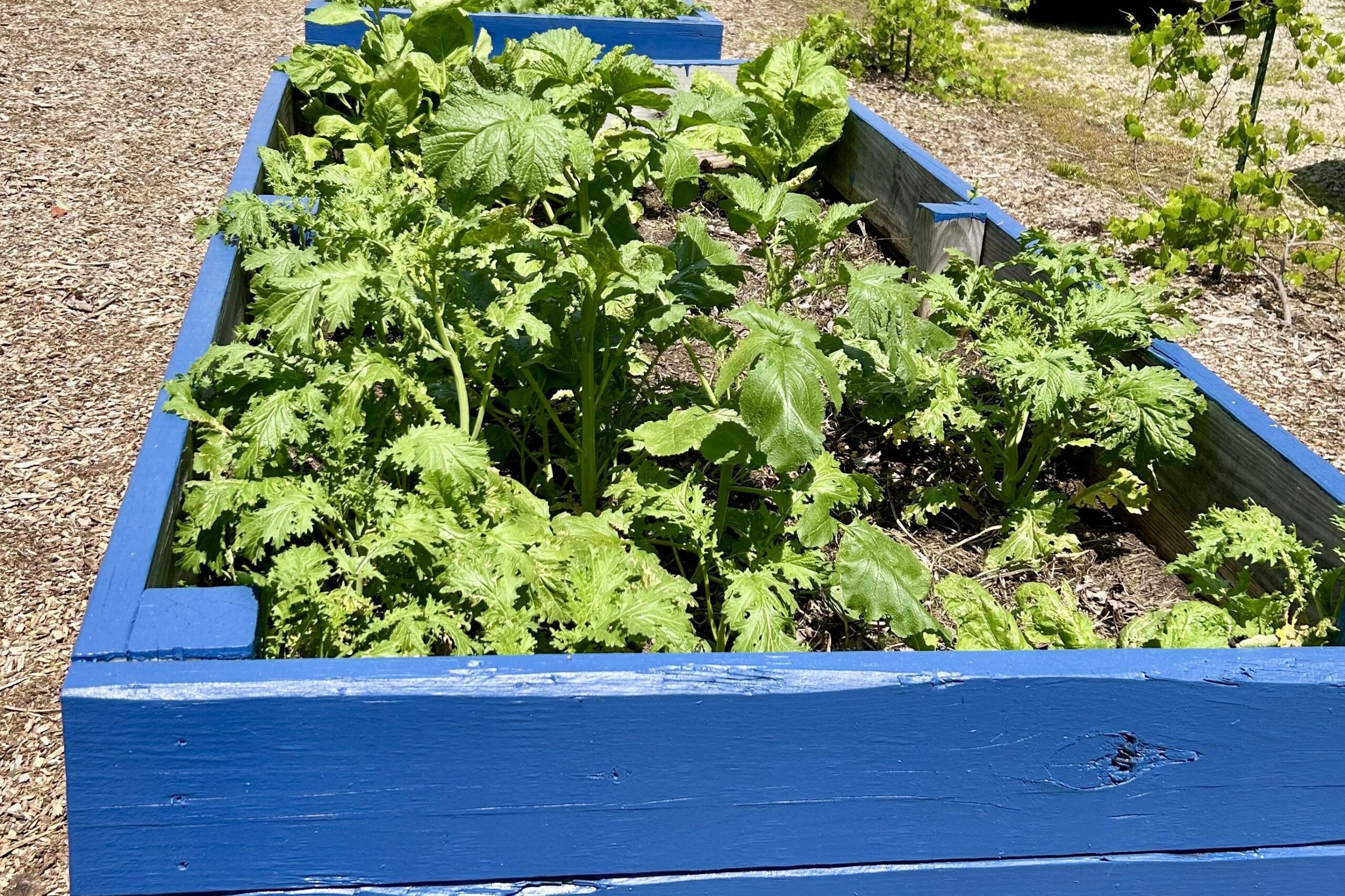

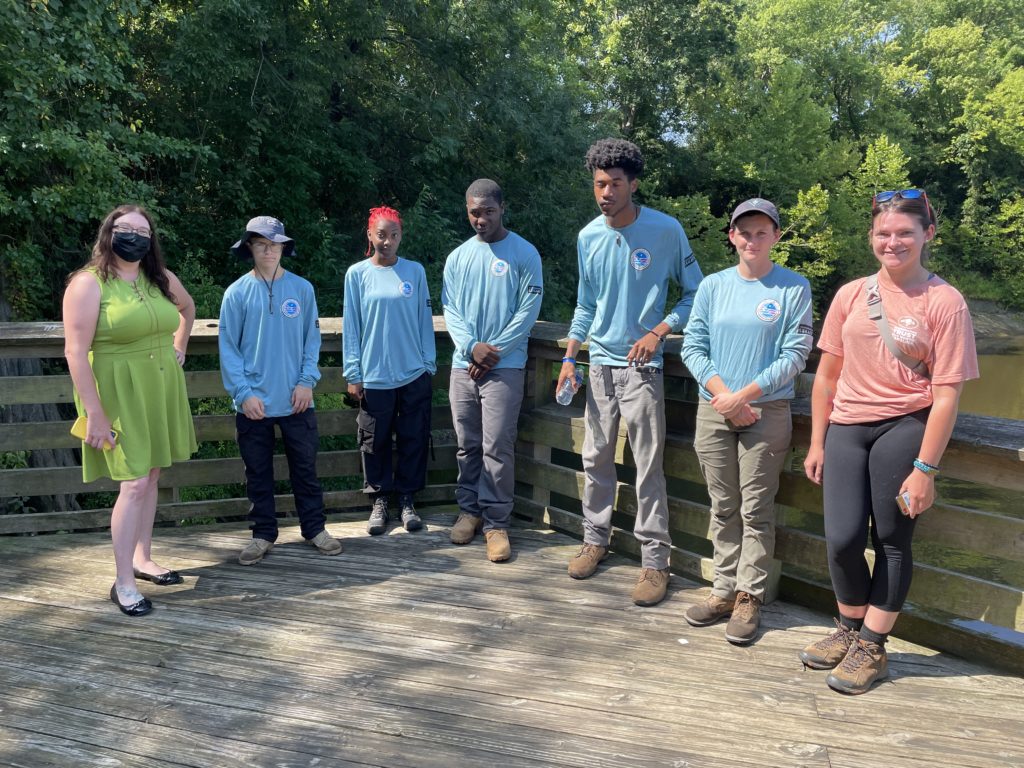
CTNC was honored to have played a role in turning a community garden idea into a reality. CTNC’s Resilience Corps NC service member, Anyah Brown, has assisted with the creation of the garden throughout her term.
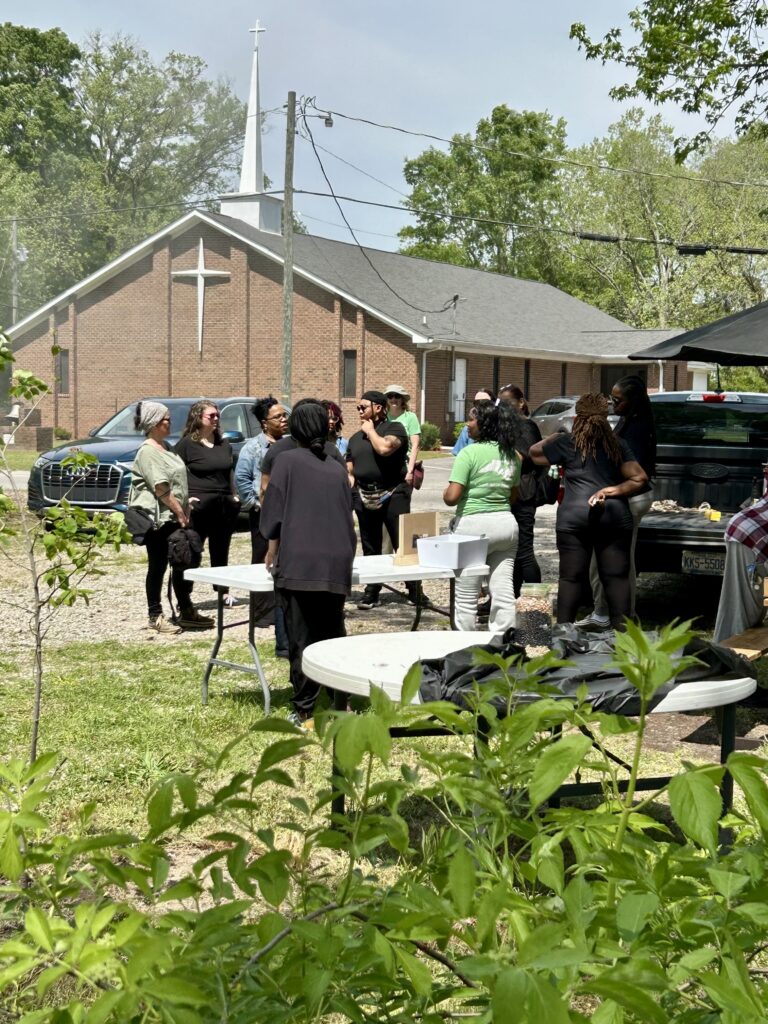

Mayor Bobbie Jones and Commissioners Vananza Brown, Joe Myrick, and Lee Staton shared their support for this collaborative achievement through their time and attention. Cynthia Satterfield, Erin Witcher, and Beth Mullenberg joined the celebration as representatives for CTNC, highlighting the tangible difference made by Resilience Corps NC in North Carolina communities.
This area dedicated to growing fresh and healthy food and connecting with others will foster a greater sense of community in the Town of Princeville for generations to come.